Need EV Stations
Ready to convert your property to an income source with Electric Charging Stations? Our team of expert consultants assist with grants writing, asset management and EV station installs. We’ve got real people ready to give you answers.
Why Partner with Citrine?
With Citrine, you gain a partner who understands the intricacies of EV charging solutions and the importance of precise project management. Our approach focuses on delivering high-quality installations that enhance property value, support sustainability goals, and provide significant returns on investment.
Our Products
FAQ
Have any questions? We can help answer them.
What is OCPP?
OCPP (Open Charge Point protocol) is a shared language which is used by EV Charger and software management platforms to communicate to each other. Not all electric vehicle chargers are OCPP compliant. But the ones who are enjoy a wide selection of features.
What circuit size is required for my EV charger?
To connect a 32A EV charging station, you need to have a 40A circuit breaker available. For a 40A EV charger - 50A circuit breaker and 48A EV charger - 60A circuit breaker.
What is a Level 2 EV charger?
EV chargers are categorized by levels:
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- DCFC (DC Fast Charger)
A Level 2 charger is a high-power rate option that can charge your vehicle in less time than a Level 1 charger while still being suitable for residential and commercial applications. DCFCs, on the contrary, are mainly reserved for large commercial and industrial applications.
Do all EVs use the same connector?
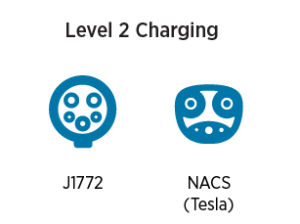
All Level 1 and Level 2 chargers feature a standard plug or connector, receiving the name of Type 1 connector.
A Type 1 connector is an international standard plug known as the SAE J1772 connector or simply as a J connector.
But this is not the case for DC Fast Chargers (DCFCs) or Level 3 Chargers. They tend to feature different plugs with a common type being the NACS connector.
NACS (North American Charging Standard), developed by Tesla but open-sourced to all automakers, chargers prioritize DC charging, enabling much faster charging times compared to the traditional J1772 standard that delivers AC power from residential and smaller commercial chargers. The NACS connector is on it way to becoming a standardized connector for all auto manufacturers in the coming year to increase charging inclusivity. This emphasis on rapid charging enhances the overall charging experience for non-Tesla cars, particularly during long-distance travel.
How fast are Level 2 EV Chargers?
The Level 2 chargers are extremely fast compared to regular Level 1 chargers. The most 240V charging station features a power rate of 7.5kW, but Level 2 chargers can feature power ratings from 3kW to 20kW. Charging speed in kilowatt-hour per mile varies between EV models. For instance a Tesla Model 3 could get as much as 83 miles of charge in a single hour and could be fully charged in 3 hours.
What is different between Level 1, 2, 3 and 4 EV Chargers?
Consider the battery capacity of the vehicles that will use the charger.
- Nissan Leaf - 40kWh
- Sprinter Panel Van - 125kWh
- Freightliner eCascadia Semi - 550kWh
Consider the EV charger's capacity.
- Power
- Level 1 AC: 1-1.8kW
- Level 2 AC: 3-22kW
- Level 3/DCFC: 30-360kW
- Level 4 (DCFC): >1MW
- Current passenger vehicle charging at 25-350kW of power
- Next-generation medium- to heavy-duty vehicle charging equipment is already pushing >1MW
Consider the scale of the fleet.
- How many vehicles will need to be charging at once?
Connect With Us
Ready to optimize your property with Citrine? Contact us through our social media, email, or give us a call. Our customer support team is eager to provide personalized guidance and answer any questions you may have.